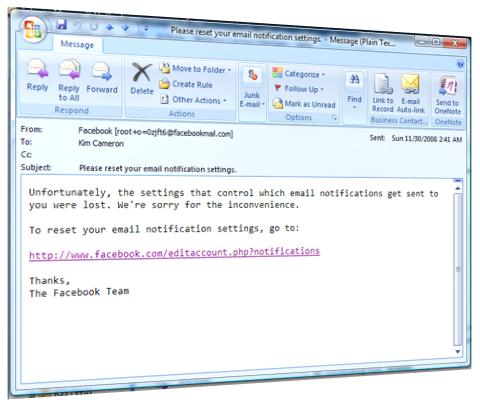
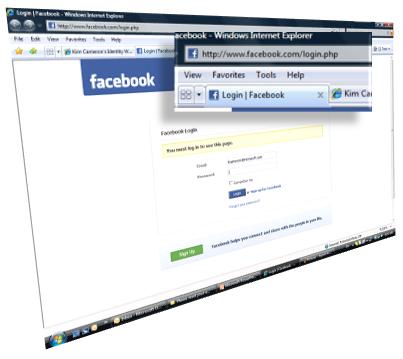
My friend Jerry Fishenden, Microsoft's National Technology Officer in the United Kingdom, had a piece in The Scotsman recently where he lays out, with great clarity, many of the concerns that “keep me up at night”. I hope this kind of thinking will one day be second nature to policy makers and politicians world wide.
Barely a day passes it seems without a new headline appearing about how our personal information has been lost from yet another database. Last week, the Information Commissioner, Richard Thomas, revealed that the number of reported data breaches in the UK has soared to 277 since HMRC lost 25 million child benefit records nearly a year ago. “Information can be a toxic liability,” he commented.
Such data losses are bad news on many fronts. Not just for us, when it's our personal information that is lost or misplaced, but because it also undermines trust in modern technology. Personal information in digital form is the very lifeblood of theinternet age and the relentless rise in data breaches is eroding public trust. Such trust, once lost, is very hard to regain.
Earlier this year, Sir James Crosby conducted an independent review of identity-related issues for Gordon Brown. It included an important underlying point: that it's our personal data, nobody else's. Any organisation, private or public sector, needs to remember that. All too often the loss of our personal information is caused not by technical failures, but by lackadaisical processes and people.
These widely-publicised security and data breaches threaten to undermine online services. Any organisations, including governments, which inadequately manage and protect users’ personal information, face considerable risks – among them damage to reputation, penalties and sanctions, lost citizen confidence and needless expense.
Of course, problems with leaks of our personal information from existing public-sector systems are one thing. But significant additional problems could arise if yet more of our personal information is acquired and stored in new central databases. In light of projects such as the proposed identity cards programme, ContactPoint (storing details of all children in the UK), and the Communications Data Bill (storing details of our phone records, e-mails and websites we have visited), some of Richard Thomas's other comments are particularly prescient: “The more databases set up and the more information exchanged from one place to another, the greater the risk of things going wrong. The more you centralise data collection, the greater the risk of multiple records going missing or wrong decisions about real people being made. The more you lose the trust and confidence of customers and the public, the more your prosperity and standing will suffer. Put simply, holding huge collections of personal data brings significant risks.”
The Information Commissioner's comments highlight problems that arise when many different pieces of information are brought together. Aggregating our personal information in this way can indeed prove “toxic”, producing the exact opposite consequences of those originally intended. We know, for example, that most intentional breaches and leaks of information from computer systems are actually a result of insider abuse, where some of those looking after these highly sensitive systems are corrupted in order to persuade them to access or even change records. Any plans to build yet more centralised databases will raise profound questions about how information stored in such systems can be appropriately secured.
The Prime Minister acknowledges these problems: “It is important to recognise that we cannot promise that every single item of information will always be safe, because mistakes are made by human beings. Mistakes are made in the transportation, if you like – the communication of information”.
This is an honest recognition of reality. No system can ever be 100 per cent secure. To help minimise risks, the technology industry has suggested adopting proposals such as “data minimisation” – acquiring as little data as required for the task at hand and holding it in systems no longer than absolutely necessary. And it's essential that only the minimum amount of our personal information needed for the specific purpose at hand is released, and then only to those who really need it.
Unless we want to risk a domino effect that will compromise our personal information in its entirety, it is also critical that it should not be possible automatically to link up everything we do in all aspects of how we use the internet. A single identifying number, for example, that stitches all of our personal information together would have many unintended, deeply negative consequences.
There is much that governments can do to help protect citizens better. This includes adopting effective standards and policies on data governance, reducing the risk to users’ privacy that comes with unneeded and long-term storage of personal information, and taking appropriate action when breaches do occur. Comprehensive data breach notification legislation is another important step that can help keep citizens informed of serious risks to their online identity and personal information, as well as helping rebuild trust and confidence in online services.
Our politicians are often caught between a rock and a very hard place in these challenging times. But the stream of data breaches and the scope of recent proposals to capture and hold even more of our personal information does suggest that we are failing to ensure an adequate dialogue between policymakers and technologists in the formulation of UK public policy.
This is a major problem that we can, and must, fix. We cannot let our personal information in digital form, as the essential lifeblood of the internet age, be allowed to drain away under this withering onslaught of damaging data breaches. It is time for a rethink, and to take advantage of the best lessons that the technology industry has learned over the past 30 or so years. It is, after all, our data, nobody else's.
My identity has already been stolen through the very mechanisms Jerry describes. I would find this even more depressing if I didn't see more and more IT architects understanding the identity domino problem – and how it could affect their own systems.
It's our job as architects to do everything we can so the next generation of information systems are as safe from insider attacks as we can make them. On the one hand this means protecting the organizations we work for from unnecessary liability; on the other, it means protecting the privacy of our customers and employees, and the overall identity fabric of society.
In particular, we need to insist on:
- scrupulously partitioning personally identifying information from operational and profile data;
- eliminating “rainy day” collection of information – the need for data must always be justifiable;
- preventing personally identifying information from being stored on multiple systems;
- use of encryption;
- minimal disclosure of identity intormation within a “need-to-know” paradigm.
I particularly emphasize partitioning PII from operational data since most of a typical company's operational systema – and employees – need no access to PII. Those who do need such access rarely need to know anything beyond a name. Those who do need greater access to detailed information rarely need access to information about large numbers of people except in anonymized form.
I would love someone to send me a use case that calls for anyone to have access – at the same time – to the personally identifying information about thousands of individuals (much less millions, as was the case for some of the incidents Jerry describes). This kind of wholesale access was clearly afforded the person who stole my identity. I still don't understand why.
 First of all, I have to refer readers to the Office of Inadequate Security, apparently operated by databreaches.net. I suggest heading over there pretty quickly too – the office is undoubtedly going to be so busy you'll have to line up as time goes on.
First of all, I have to refer readers to the Office of Inadequate Security, apparently operated by databreaches.net. I suggest heading over there pretty quickly too – the office is undoubtedly going to be so busy you'll have to line up as time goes on.